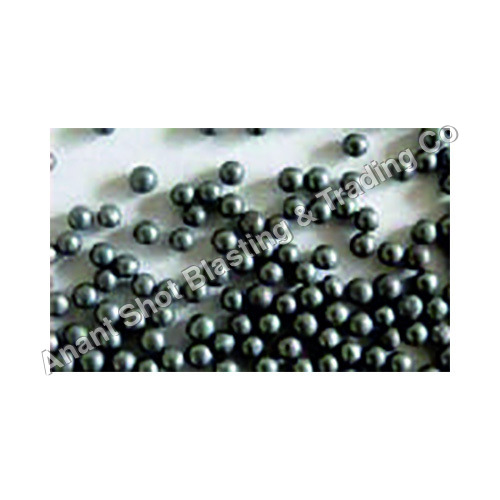
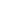
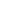
Steel Shot
Product Details:
- Color Silver
- Weight As per requirement Kilograms (kg)
- Usage Industrial
- Material Steel
- Type Powder
- Grain Sizes Small
- Click to View more
Steel Shot Price And Quantity
- 100 Kilograms
Steel Shot Product Specifications
- As per requirement Kilograms (kg)
- Steel
- Powder
- Industrial
- Silver
- Small
Steel Shot Trade Information
- Cash in Advance (CID)
- 5000 Kilograms Per Month
- 7 Days
- All India
Product Description
What is Steel Shot? Steel shot is made from carbon steel and is manufactured by melting steel and then forcing it through a mold to form small, round particles (shots). These shots are used in shot blasting machines to clean or prepare surfaces.
- Shape: Steel shot is spherical (round), which helps it produce a smooth, uniform surface finish. The round shape is ideal for cleaning, peening, and polishing metal surfaces.
- Hardness: Steel shot is typically harder than other abrasives, such as sand or glass beads. Its hardness allows it to effectively remove rust, scale, old paint, and other contaminants from metal surfaces.
- Durability: Steel shot is very durable, and because its made of steel, it can be reused multiple times without degrading. This is a cost-effective feature since the shot can be recycled in a blasting machine.
- Size: Steel shot comes in a variety of sizes, ranging from fine (for light cleaning or polishing) to large (for heavy-duty cleaning or rust removal). The size selection depends on the specific application and the level of abrasiveness needed.
- Low-carbon Steel Shot: More ductile and less prone to breakage, low-carbon steel shot is used for processes like shot peening, where a gentler impact is desired to improve the surface fatigue resistance of a part.
- tainless Steel Shot: While more expensive than regular steel shot, stainless steel shot is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for applications where rust-free or non-ferrous materials are critical, like in aerospace or food processing industries.
- Reusability: Steel shot can be reused many times before it breaks down or becomes too worn to be effective, which reduces operational costs.
- Effective Cleaning: Its hardness and durability allow it to remove stubborn contaminants and provide excellent surface finishes.
- Consistency: Steel shot provides consistent results and can be controlled for specific finishing needs, making it versatile across different applications.
- Steel shot comes in a range of sizes, each suited for different types of shot blasting applications. The size of the steel shot used directly impacts the results of the blasting process, including the speed of cleaning, the level of abrasion, and the type of surface finish achieved.
Fine/Small Sizes:
- S-230 (around 0.18 mm / 0.007 inches)
- S-280 (around 0.22 mm / 0.009 inches)
- S-330 (around 0.25 mm / 0.010 inches)
- S-390 (around 0.30 mm / 0.012 inches)
- S-460 (around 0.35 mm / 0.014 inches)
- S-550 (around 0.40 mm / 0.016 inches)
- S-660 (around 0.46 mm / 0.018 inches)
- S-780 (around 0.50 mm / 0.020 inches)
- S-880 (around 0.55 mm / 0.022 inches)
Surface Condition:
- For heavy-duty cleaning or rust removal, larger shot sizes are preferred, as they have more mass and can remove tougher contaminants faster.
- Smaller shot sizes are best for light cleaning or polishing, as they offer a gentler impact that wont damage the surface.
- Softer materials or thin components may require smaller shot sizes to avoid damage.
- Tougher materials can handle larger shot sizes without risk of deformation.
- If you are aiming for a smooth finish, such as polishing or fine cleaning, smaller shot sizes like S-280 or S-330 are ideal.
- If a rougher surface or more aggressive cleaning is required, larger shot sizes are better.
Blasting Pressure: The size of the shot affects how fast it can be accelerated by the blast wheels or nozzles. Larger shot sizes generally require more air or wheel power to effectively propel them, so adjusting blasting pressure might be necessary.
Reusability: Smaller steel shots may break down more quickly than larger ones, as they face more stress during the blasting process. In high-volume applications, you may need to replace smaller shot sizes more frequently.
Conclusion: Choosing the right steel shot size depends on the specific requirements of your application, including the type of surface being treated, the material, and the desired finish. Smaller shots are used for light cleaning and polishing, while larger shots are used for heavy-duty cleaning or surface treatment like shot peening. Understanding these size options ensures that your shot blasting process will be both efficient and effective.
Media Blasting Is Done by An Air-powered Gun Which Will Propel Silica Sand Toward a Surface at A High Rate of Speed. Compressed Air Is Used to Supply the Power to The Gun, And the Sand Is Forced Out of a Barrel Which Will Direct It Toward Your Target.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+